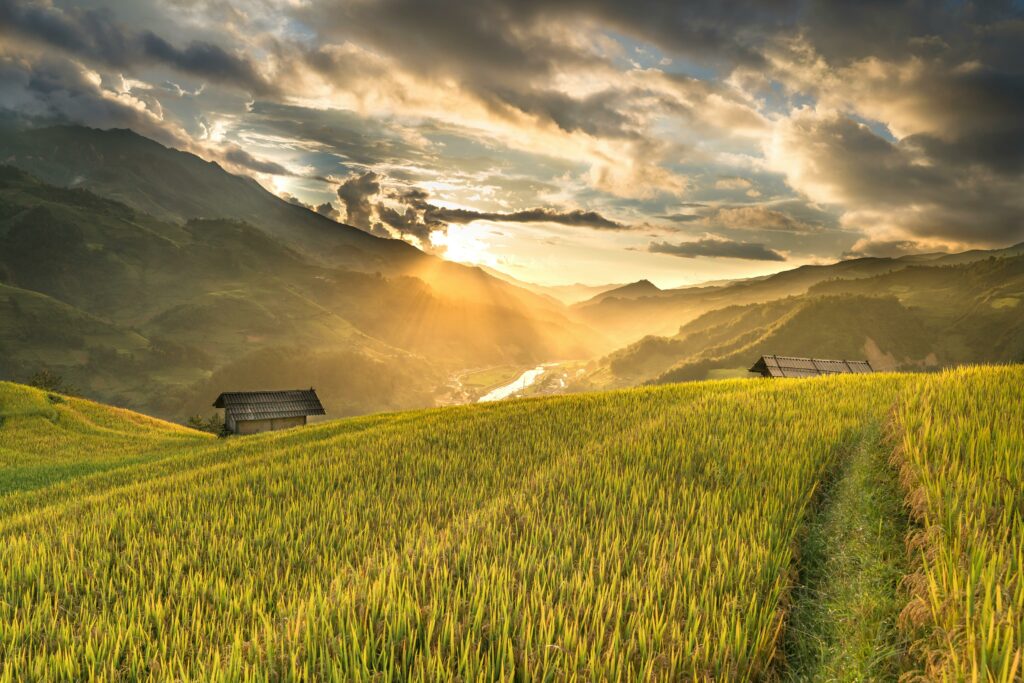
Since agricultural operations in Wyoming have been significantly impacted by recent wildfires, the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) is offering technical and financial assistance to help farmers and livestock producers recover from these adverse weather events.
Impacted producers should contact their local USDA Service Center to report losses and learn more about program options available to assist in their recovery from crop, land, infrastructure, and livestock losses and damages.
USDA Disaster Assistance
Producers who experience livestock deaths in excess of normal mortality or sell injured livestock at a reduced price may be eligible for the Livestock Indemnity Program (LIP). To participate in LIP, producers will have to provide acceptable documentation of death losses or evidence of reduced sales resulting from an eligible adverse weather event and must submit a notice of loss to the USDA Farm Service Agency (FSA) no later than the annual program payment application date, which is 60 calendar days following the calendar year in which the loss occurred. The LIP payment application and notice of loss deadline is March 3, 2025, for 2024 calendar year losses. Livestock producers who experience losses related to wildfire should check with their local FSA office for LIP eligibility criteria.
Meanwhile, the Emergency Assistance for Livestock, Honeybees, and Farm-Raised Fish Program (ELAP) provides eligible producers with compensation for feed and grazing losses, transportation of feed to livestock, and hauling livestock to forage or other grazing acres. For ELAP, producers are required to complete a notice of loss and a payment application to their local FSA office no later than the annual program application deadline, Jan. 30, 2025, for 2024 calendar year losses.
Additionally, eligible orchardists and nursery tree growers may be eligible for cost-share assistance through the Tree Assistance Program (TAP) to replant or rehabilitate eligible trees, bushes or vines. TAP complements the Noninsured Crop Disaster Assistance Program (NAP) or crop insurance coverage, which covers the crop but not the plants or trees in all cases. For TAP, a program application must be filed within 90 days of the disaster event or the date when the loss of the trees, bushes or vines is apparent.
“Based on your reported losses or damages, our local Farm Service Agency county office staff are ready to help connect you with the programs best suited to meet your wildfire recovery needs” said Bill Bunce, State Executive Director for FSA in Wyoming. “Our staff will do our best to work with the loss documentation you have available. We understand that these are trying times, and you’re pulled in many directions, so when you’re able, please get in touch with us to begin the reporting process. The sooner we have the information, the sooner we can get county committee action on your requests for assistance. Examples of loss documentation include but are not limited to farm records, herd inventory, receipts and pictures of damages or losses.”
FSA also offers a variety of direct and guaranteed farm loans, including operating and emergency farm loans, to producers unable to secure commercial financing. Producers in counties with a primary or contiguous disaster designation may be eligible for low interest emergency loans to help them recover from production and physical losses. Loans can help producers replace essential property, purchase inputs like livestock, equipment, feed and seed, cover family living expenses or refinance farm-related debts and other needs.
Additionally, FSA offers several loan servicing options available for borrowers who are unable to make scheduled payments on their farm loan programs debt to the agency because of reasons beyond their control.
The Farm Storage Facility Loan Program (FSFL) provides low-interest financing so producers can build, repair, replace or upgrade facilities to store commodities. Loan terms vary from three to 12 years. Producers who incurred damage to or loss of their equipment or infrastructure funded by the FSFL program should contact their insurance agent and their local USDA Service Center. Producers in need of on-farm storage should also contact USDA.
Risk Management
Producers who have risk protection through Federal Crop Insurance or FSA’s NAP should report crop damage to their crop insurance agent or FSA office, respectively. If they have crop insurance, producers should provide a notice of loss to their agent within 72 hours of initial discovery of damage and follow up in writing within 15 days.
For NAP covered crops, a Notice of Loss (CCC-576) must be filed within 15 days of the loss becoming apparent, except for hand-harvested crops, which should be reported within 72 hours.
“Because there is always the possibility of losses from wildfires and other natural disasters, USDA offers crop insurance and risk management to help producers mitigate the financial impact of losses resulting from disaster events, like these, that are beyond their control,” said Eric Bashore, Director of RMA’s Regional Office that covers Wyoming. “Times of disaster can be a trying time for producers, and they should stay in close contact with their crop insurance agent. Producers can be assured that the Approved Insurance Providers, loss adjusters, and agents are experienced and well-trained in handling these types of events. “
Conservation
Outside of the primary nesting season, emergency and non-emergency haying and grazing of Conservation Reserve Program (CRP) acres may be authorized to provide relief to livestock producers in areas affected by a severe drought or similar natural disasters. Producers interested in haying or grazing of CRP acres should contact their county FSA office to determine eligibility.
FSA’s Emergency Conservation Program (ECP) can assist landowners with financial and technical assistance to remove debris from farmland such as woody material, sand, rock and materials from collapsed hoop houses/high tunnels on cropland or pastureland. Through the program, FSA can provide assistance toward the restoration or replacement of fences including livestock cross fences, boundary fences, cattle gates or wildlife exclusion fences on agricultural land.
Additionally, the Emergency Forest Restoration Program (EFRP) can assist eligible owners of nonindustrial private forestland to also restore the land by removing debris, repairing forestland roads, and replacing fence. For both programs, farmers and ranchers should check with their local FSA office to find out about sign-up periods, which are set by the FSA County Committee.
USDA’s Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS) is always available to provide technical assistance during the recovery process by assisting producers to plan and implement conservation practices on farms, ranches and working forests impacted by natural disasters. The Environmental Quality Incentives Program (EQIP) can help producers plan and implement conservation practices on land impacted by natural disasters.
“At USDA, we serve as a partner to help landowners with their resiliency and recovery efforts,” said Jackie Byam, NRCS State Conservationist in Wyoming. “Our staff will work one-on-one with landowners to make assessments of the damages and develop methods that focus on effective recovery of the land.”
Assistance for Communities
Additional NRCS programs include the Emergency Watershed Protection (EWP) program, which assists local government sponsors with the cost of addressing watershed impairments or hazards such as debris removal and streambank stabilization.
The EWP Program is a recovery effort aimed at relieving imminent hazards to life and property caused by floods, fires, windstorms and other natural disasters. All projects must have an eligible project sponsor. NRCS may bear up to 75% of the eligible construction cost of emergency measures (90% within county-wide limited-resource areas as identified by the U.S. Census data). The remaining costs must come from local sources and can be in the form of cash or in-kind services.
EWP is designed for installation of recovery measures to safeguard life and property as a result of a natural disaster. Threats that the EWP Program addresses are termed watershed impairments. These include, but are not limited to:
- Debris-clogged waterways.
- Unstable streambanks.
- Severe erosion jeopardizing public infrastructure.
- Wind-borne debris removal.
Eligible sponsors include cities, counties, towns or any federally recognized Native American tribe or tribal organization. Sponsors must submit a formal request (by mail or email) to the NRCS state conservationist for assistance within 60 days of the natural disaster occurrence or 60 days from the date when access to the sites become available. For more information, please contact your local NRCS office.
In addition to EWP, Conservation Technical Assistance (CTA) is another valuable service that NRCS can provide following a wildfire. NRCS technical assistance can help fire victims with planning cost-effective post fire restoration practices.
More Information
Additional USDA disaster assistance information can be found on farmers.gov, including USDA resources specifically for producers impacted by wildfire. Those resources include the Disaster Assistance Discovery Tool, Disaster-at-a-Glance fact sheet, Loan Assistance Tool, and Natural Disasters and Crop Insurance fact sheet. Additionally, FarmRaise offers an FSA educational hub with LIP and ELAP decision tools as well as farm loan resource videos. For FSA and NRCS programs, producers should contact their local USDA Service Center. For assistance with a crop insurance claim, producers and landowners should contact their crop insurance agent.
USDA touches the lives of all Americans each day in so many positive ways. Under the Biden-Harris administration, USDA is transforming America’s food system with a greater focus on more resilient local and regional food production, fairer markets for all producers, ensuring access to safe, healthy and nutritious food in all communities, building new markets and streams of income for farmers and producers using climate smart food and forestry practices, making historic investments in infrastructure and clean energy capabilities in rural America, and committing to equity across the Department by removing systemic barriers and building a workforce more representative of America. To learn more, visit usda.gov.