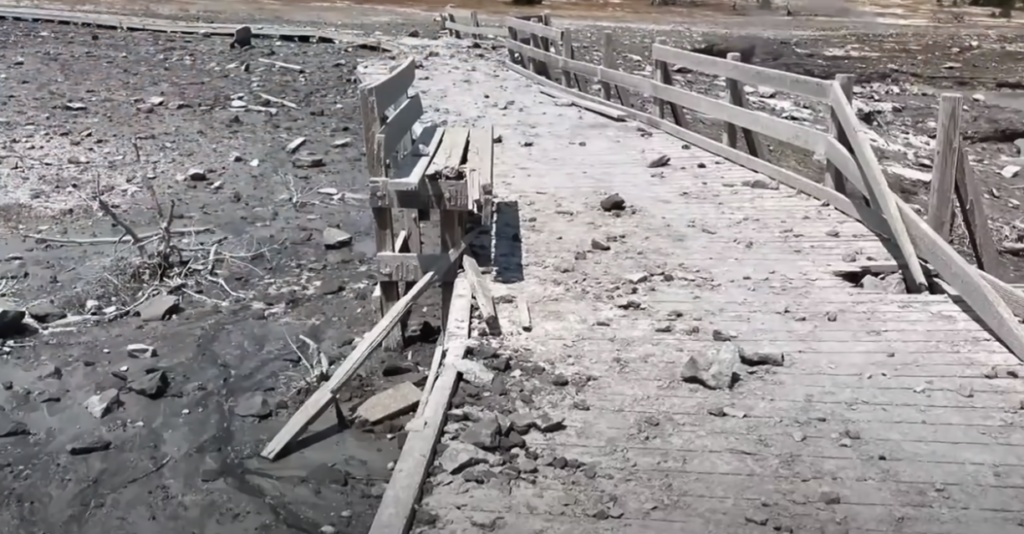
The National Park Service is updating the conditions of the area around the Biscuit Basin area of Yellowstone National Park, after an unexpected geyser explosion sent people running frantically to avoid being hit by water, ash, rocks, and debris earlier this week.
National Park Service (NPS) field crews have completed a preliminary assessment of the conditions following the hydrothermal explosion at Black Diamond Pool. For a map showing the locations of the features in that area, click here.
What happened?
The July 23, 2024, hydrothermal explosion at Biscuit Basin resulted from water suddenly transitioning to steam in the shallow hydrothermal system beneath Black Diamond Pool and was not caused by volcanic activity. Seismicity, ground deformation, and gas and thermal emissions remain at their normal background levels, and there were no detectable precursors to this event.
The explosion, which sent steam and debris to a height of hundreds of feet above the ground, destroyed a nearby boardwalk and ejected grapefruit-sized rocks tens to hundreds of feet from the source. Some blocks closest to the explosion site are about 3 feet (1 meter) wide and weigh hundreds of pounds. The explosion was largely directed to the northeast toward the Firehole River, and the largest blocks of debris fell in that direction. The dark color of the explosion was a result of mud and debris mixed with steam and boiling water. Although visitors were present at the time of the event, no injuries were reported.
Black Diamond Pool and Black Opal Pool were affected by Tuesday’s explosion, and while they remain distinct features, the shape of Black Diamond has changed somewhat. Both pools are murky due to debris, and the unstable ground around their edges occasionally slides into the water. Just after the eruption, Black Diamond Pool exhibited minor roiling and water spouting. The water level in the pool rose over the course of the day, and by Tuesday afternoon the roiling transitioned to occasional bursts of hot water that reached about 8 feet (2.4 meters) in height.
What is happening now?
By Wednesday morning, July 24, the levels of Black Diamond Pool and Black Opal Pool had risen enough that both were overflowing and sending murky water into the Firehole River. No water bursts from Black Diamond Pool were witnessed Wednesday morning.
What are ongoing hazards?
Given the recent changes to the hydrothermal plumbing system, small explosions of boiling water from this area in Biscuit Basin continue to be possible over the coming days to months. USGS and NPS geologists will be monitoring conditions, mapping the debris field, and sampling water to assess any changes in the shallow hydrothermal system over the next several days.
Hydrothermal explosions typically occur in the park one to a few times per year, but often in the back country where they may not be immediately detected.
Similar, although smaller, hydrothermal explosions took place in 1989 at Porkchop Geyser in Norris Geyser Basin, and on April 15, 2024, from the Porcelain Terrace Area of Norris Geyser Basin. A small hydrothermal explosion occurred from Wall Pool, in Biscuit Basin, in 2009. Significant hydrothermal explosions, probably similar in size to that of July 23, 2024, occurred in the 1880s at Excelsior Geyser, in Midway Geyser Basin.
Yellowstone National Park has closed Biscuit Basin for the remainder of the 2024 season for visitor safety. Grand Loop Road remains open to vehicles, and other nearby thermal basins, like Black Sand Basin, are open. Additional Yellowstone National Park information about visitor access can be found here.